 The sewing machine appeared on domestic shelves in the middle of the twentieth century and incredibly quickly became an integral assistant in every Soviet family. This technical tool has successfully replaced the needle and thread in the hands of a seamstress. The sewing machine has not stopped in its perfection, and today the market is full of amazing copies of machines that can be used by an ordinary layman who has absolutely no sewing skills.
The sewing machine appeared on domestic shelves in the middle of the twentieth century and incredibly quickly became an integral assistant in every Soviet family. This technical tool has successfully replaced the needle and thread in the hands of a seamstress. The sewing machine has not stopped in its perfection, and today the market is full of amazing copies of machines that can be used by an ordinary layman who has absolutely no sewing skills.
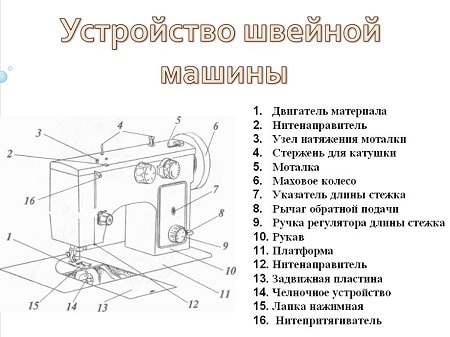
The internal structure of the sewing machine
An ordinary user sees only a shell, under which a cunning mechanism is hidden, which we will now talk about.
Perhaps the most important detail in any, even the most modern sewing machine, is the shuttle. The shuttle is a working part of a typewriter, which is made, as a rule, of wood and was also used in weaving machines. It serves for shifting transverse threads in the process of making fabric.
Let's consider in detail how the main mechanisms interact with the shuttle and the inside of the entire machine works. Under the needle behind the sliding door (located at the bottom), there is a hairpin, carefully remove this part with a slight movement towards ourselves and up. Sometimes, for this, it is necessary to deflect the grip aside.

![]() See also - The best sewing machines for the home: reviews and expert opinion
See also - The best sewing machines for the home: reviews and expert opinion
Technical features
A spool of thread is located inside the pin. The thread is stretched in such a way that when the flywheel turns, it fits parallel to the upper thread.
The tension of the lower thread adjusts the screw, which is located on the pin, it is important to remember that if the upper and lower thread are too tight, this will lead to inevitable frequent breaks. The optimal tension is slightly tighter than average so that the thread does not sag. The shuttle pulls the thread in the same way.
On the spool, which we have already mentioned, there are usually slots and notches. They are mainly used to wind the thread onto the drive. This does not always apply, for a special mode of operation.
If you carefully examine the hairpin, you can see a protrusion, it is he who plays the role of a latch, not allowing the hairpin to turn together with the coil.
The part that rotates around the pin is the same shuttle. The mechanism ensures its stable movement along a given trajectory. Even a small deflection in the movement of the shuttle will result in uneven transverse thread overlap.
Adjustment, thread tension
The first thing we need is to pay attention to the needle holder. It has holes for bolts on both sides, it is with them that it is fixed. One has a flat head, which is what we need for adjustment. This happens by pulling it out. But first, you need to move the needle a little, moving it away from the hook, this gap allows you to make the adjustment.The gap is very small and this space is quite enough to rebuild the mechanism, as the performer needs. It is important that when changing the gap, it is very problematic to return it to its previous state.
It is important to place the thread correctly in the needle holders. The fact is that the needle is inherently uneven, if you take it and turn it over, then a gap forms on the other side, which cannot be allowed. The distance to the shuttle in a new sewing machine does not exceed 0.15 mm, and if the needle is incorrectly set, it increases up to a millimeter. This effect is due to the flattened edge at the end of the needle and must be correctly positioned in the needle holder. Such a sewing machine device is universal, regardless of the price and manufacturer.
Depending on the type of sewing machine, the needle holders may be movable or static. If the needle holder is stationary, the entire hook body must be removed if adjustment is required. In this case, adjustment will be made by removing the entire body. Then, by placing washers under the attachment points, you can set an approximate gap, thanks to which the shuttle can lay the thread evenly. This adjustment option is very laborious and will not do without a considerable investment of time.

Sewing machine device
The device of the sewing machine is very difficult for a simple user who is not familiar with the design details, but the principle of operation of this unit is very simple and straightforward.
Backing the shuttle, the needle follows a predetermined trajectory and passes the upper thread downwards, inevitably twisting from the lower one. Thanks to this programmed movement of the needle lies the ability of the machine to perform complex technical patterns that are not always possible for the simple hands of a seamstress. On some models, the needle is positioned slightly to the side to create hem.
If you delve into the mechanical subtleties, then it should be said that the shaft runs in the center. It is interlocked with the flywheel axis, and on both sides of the center there are two rods that are indispensable for the operation of the machine. They constantly, synchronously rotate, activating the mechanism. The first rod has an important part that looks like a wrench, this part moves along a predetermined path along the course of the fabric. The second rod contains a cam that is inserted into the gap. It is he who is responsible for lifting this part.
In all models there is such a type of connection of several parts as "Dovetail". This connection drives the teeth. The stitch length can also be adjusted by changing the span. The swing, in turn, is changed by turning a lever that is rigidly fixed to the dovetail.
In order to adjust the upper thread, the thread must be thrown or loosened. The screw located above the needle holder in the same place is located on the eyes which does not allow the thread to loosen.
The device of the sewing machine includes such an important element as winding. If you pay attention to the flywheel, then you will notice a pressure ring (the shaft is located on it), on which there is a risk under it there is an ear with a wheel. The coil is positioned higher and is put on the pole. From the spool, the thread goes to the bobbin for winding. When the drive of the machine starts to work, the pressure ring begins to rotate. The hook also affects the thread tension, so you should monitor its condition. The speed of rotation of rotation, and, consequently, the number of stitches per unit of time in a modern machine is very high. This allows, without holding a thread in your hands, to create complex patterns in a short time, without having the skill of a seamstress. This technique has greatly simplified the work, both in large sewing factories, by reducing the sewing time, and for an ordinary housewife.
See also: