In modern life, one can no longer do without such a thing as an energy-saving lamp. As its name says, a feature of these lamps is the economical consumption of electricity, but at the same time it produces good light radiation, which naturally saves your finances. Many are interested in circuit and device of an energy-saving lampwhich we will gladly provide in this article.
Externally, an LED lamp is often not much different from a conventional one with a filament. So, for example, they have an identical base. The only difference is in the glass shell and what is under it. The housekeeper has an electric circuit inside, while an incandescent lamp has only two contacts and a tungsten filament between them.
At the moment, incandescent lamps begin to gradually leave the market, in their place come luminescent and LED. In some countries, they generally ceased to be produced, but in the CIS countries they still have some popularity.
Device and principle of operation
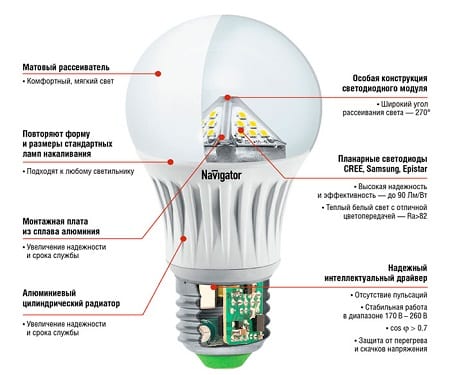
What is the secret of energy conservation of these devices. This question interests many people. However, there is nothing complicated in the design of such lamps. We can say that an energy-saving lamp is a small copy of a fluorescent lamp, which we have known since the Soviet Union. But unlike their counterparts, they are installed in a conventional cartridge and are used for both general and additional lighting.
All energy saving lamps are very similar in design and consist of several parts:
- A gas discharge tube is the part that emits light, usually made of glass;
- Case - a gas discharge tube is connected to it, the case contains a power circuit and a microcircuit;
- The base is also connected to the housing and its purpose is to create contact and supply electricity to the light bulb microcircuit.
Let's describe each detail in more detail. So, the simplest part is the discharge tube. It is made of plexiglass and gas flows through this tube, which, when in contact with electricity, emits ultraviolet light. Gas can be used in different ways: Neon, Argon, Krypton, Xenon. The shape is also given in different ways. Outside, the tube is covered with a special protective substance that is not advisable to wipe, otherwise the bulb will not work as expected.
The base of the energy-saving lamp bears the contacts for powering the lamp and the thread itself for connecting to the socket. Almost identical to an incandescent lamp, it has the same appearance and even material. in our country, lamps with the following base are common: GU10, G4, E40, E27, E14, G5.3. These plinths are used in everyday life for general and additional lighting.
The body is made of special non-combustible plastic. The lamp bulb and the base are attached to it, thus making the lamp a whole.Inside the case, as mentioned above, there is a power management and control circuit, and an anti-interference filter that protects against power surges.
![]() See also - Simple rules for saving energy at home
See also - Simple rules for saving energy at home
Disassembly and diagnostics
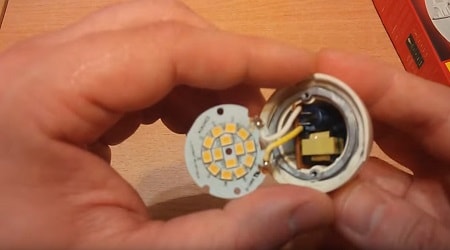
To get to the device chip, just open the housing cover. The case is divided into two parts, which are fastened together with latches and, if necessary, can be easily removed. We recommend disassembling an already unusable lamp, since when disassembling a working lamp, there is a chance to bring it into a malfunctioning state. At first glance, the lamp is solid and it is impossible to disassemble it, but this is not the case. If you carefully inspect the case, you will see a special groove, which, prying off with a knife or a screwdriver, you can easily open the case, but you need to do this without sudden movements.
After you have separated both parts from each other, you will notice that they are connected together by a pair of wires. They must also be carefully disconnected from the microcircuit, which can be done with a soldering iron by desoldering the required ends from the board. Sometimes, on some lamps, the ends of the wires are wound around the contacts, so they can simply be unscrewed. You now have two separate light bulb parts on your hands.
The electronic board is usually round and is either yellow or green. This electrical circuit is the main control device for an energy-saving lamp. If the lamp burns out, then on the board you can observe swollen and leaked capacitors, as well as burnt contacts. Four wires go to the board from the bulb, which are wound on contacts. They are usually located at the ends of the board on the opposite side from each other. In different bulbs, either a fuse or a resistor is used, which does not allow the bulb to burn out, but it burns itself. Next you can see the choke and capacitor. They adjust the flashing frequency of the lamp. The circuit itself is designed to regulate and control the ignition of the lamp, its incandescent temperature, and also to prevent voltage surges.
That's all there is to know about the design of your home energy saving lamp.
Output
Having indicated all the main aspects of the work, and the internal structure of the energy-saving lamp, we summarize - these devices are much more practical and economical than their predecessors, incandescent lamps. They are more reliable and more profitable financially. Therefore, in spite of its rather high price, we advise you to purchase these lighting devices, since they will pay off a hundredfold during their use.
We hope this article gave you an idea of what constitutes circuit and device energy-saving lamps. Be careful when choosing how to save energy in your home.

